Industrial Welding Process Automation: Advanced Solutions for Modern Industry (PART 2)
Industrial Welding Process Automation: Advanced Solutions for Modern Industry.
PART 2: KEY ELEMENTS AND IMPORTANT PRIOR DECISIONS.
We talked in the previous post that industrial welding is one of the most critical operations within the manufacturing sector, especially in industries such as automotive, infrastructure construction, and the production of electronic and aerospace components. Today, many companies are turning to automation of welding processes to improve accuracy, production speed and overall product quality.
Let's remember that automation is not just a competitive advantage, but a necessity to achieve greater efficiency and productivity while reducing human error and improving workplace safety. The implementation of industrial welding robots has transformed sectors such as automotive and heavy machinery manufacturing, where repeatability and accuracy are critical factors.
Key Elements of the Automated Welding Process
In an automated welding process there are several key elements that make the efficiency and precision of the system possible:
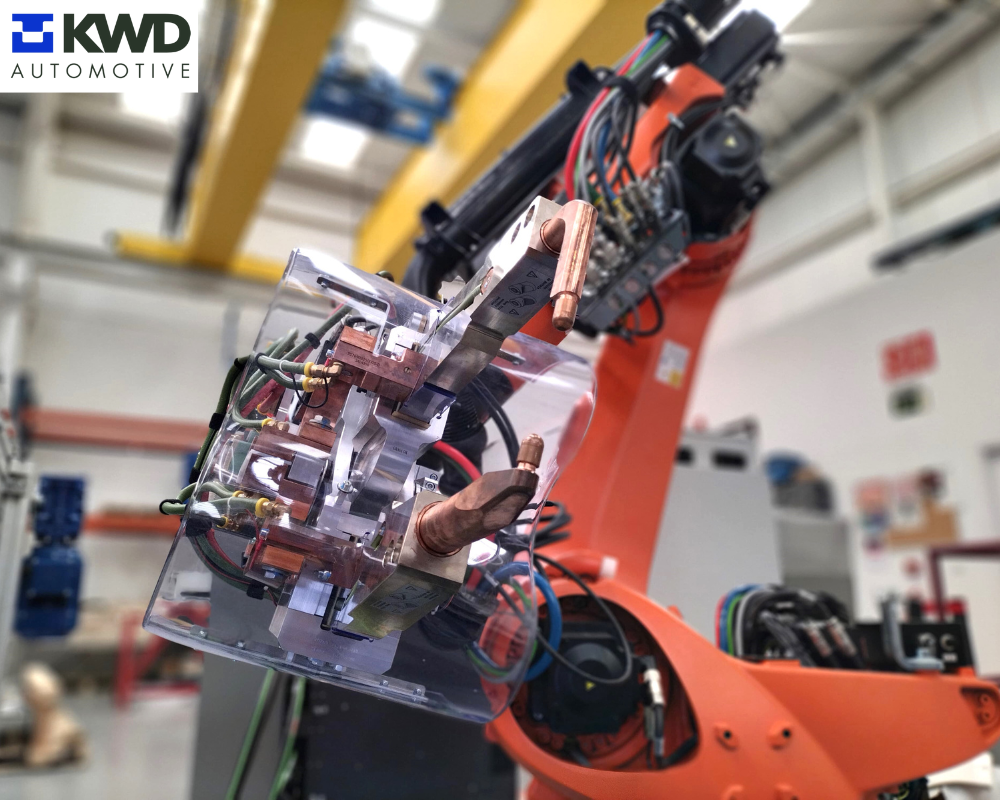
- Tooling: These are key elements in the welding process. The geometric result of each set of welded product that comes out of each tooling depends on its manufacturing, assembly and adjustment precision. They allow the correct positioning and fastening of each component to be welded, ensuring the precision and repeatability of the result obtained.
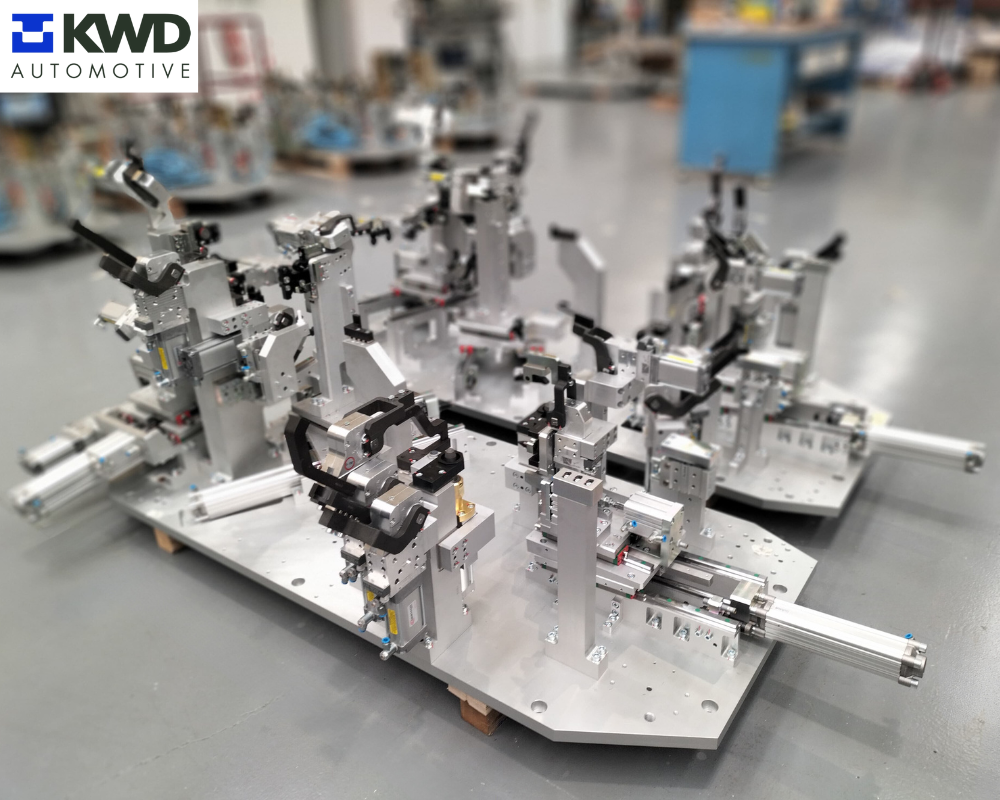

Photos: Tooling manufactured and assembled in Gurpea's facilities for the welding process automation project for KWD Automotive.
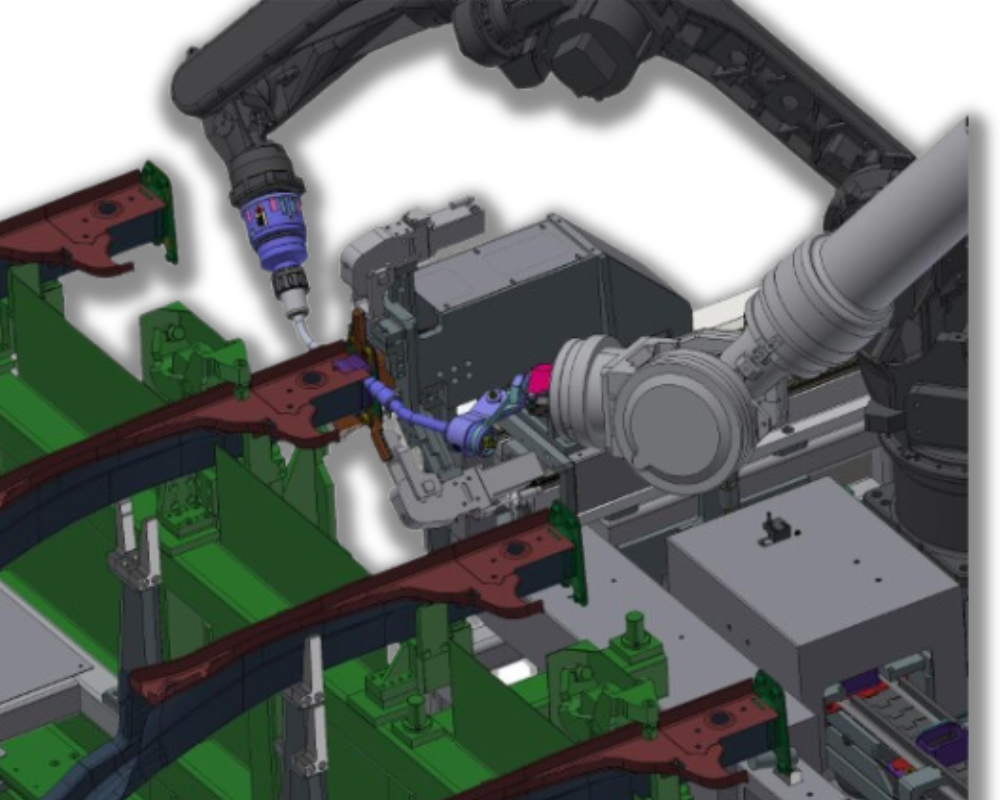
- Robots with on-board welding guns: Industrial robots are the driving force behind welding automation. Equipped with welding guns, they are capable of precise and repetitive welding at high speed, minimizing human error.
- MAG welding robots: These robots, which have special heads for the application of MAG welding, allow the application of welding seams between parts, with total control of the process, ensuring a high degree of quality.
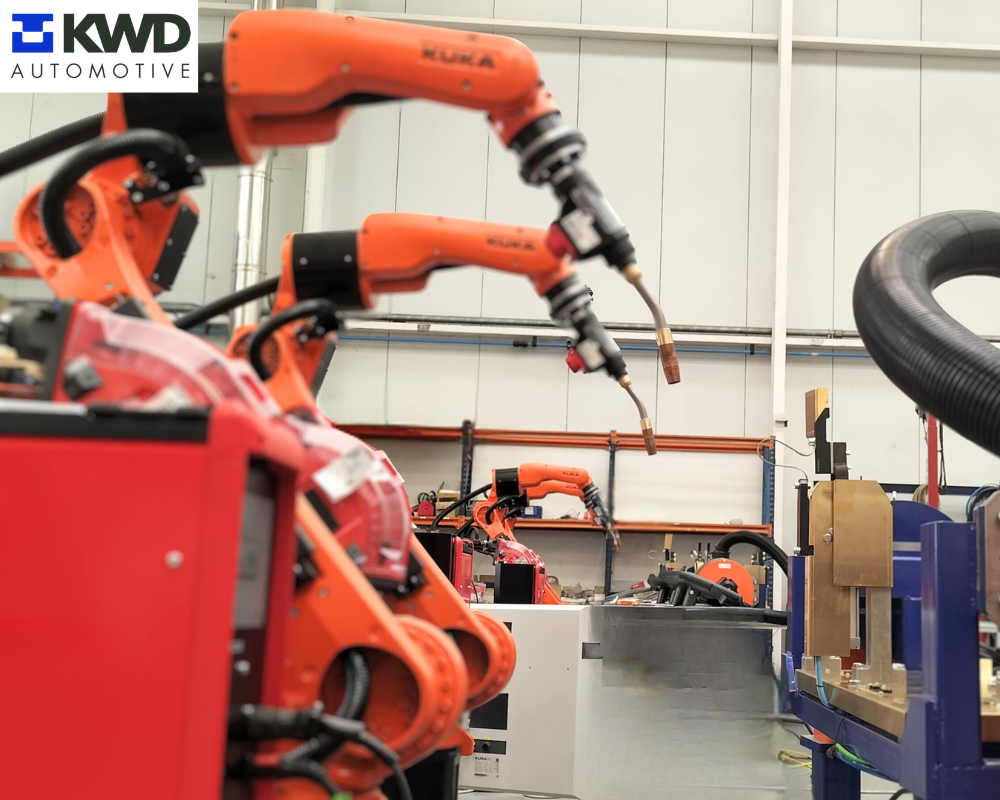

Photos: Mag welding robots assembled and programmed for the welding project for KWD Automotive.
-
Fixed spot welding clamps: Used primarily for spot weld completion, these clamps ensure that each weld spot is made accurately.
-
Resistance welding presses: These allow the welding of elements within the product assembly. Normally, these systems weld nuts or bolts included in the product assembly.
-
Automatic feeding systems: These are systems that allow feeding all the parts to the different welding presses of the automated line. They can have high part feeding rates depending on the cycle time requirements.
-
Adhesive application equipment (mastic): Equipment that allows controlled and precise dosing and application of adhesive products to the parts before welding.
How to choose an Engineering to Automate Welding Processes?
To successfully develop the automation of a welding process, it is essential to choose an engineering company that offers proven experience in similar projects and in-depth knowledge of the different types of welding and their applications to ensure the success of the project.
Gurpea's team has executed large welding projects, with installations of more than 50 robots in spaces of up to 55x50 square meters, demonstrating its ability to handle complex industrial projects.
In addition, the selected engineering company must have the capacity, and the equipment, to design customized solutions from scratch, considering customer specifications such as cycle times, production targets and available space.
It is also essential to have knowledge of advanced technology applied to welding and to offer a fluid, scalable and flexible integration that adapts to the customer's existing systems and lines, and to possible future modifications.
Grupea's comprehensive approach is a clear differentiation, as a reference supplier in the sector, since it assumes all the phases of the process: study of the project and its production objectives, design of the optimal and profitable short and long term customized solution, manufacturing, customer assembly, validation and commissioning. In addition to providing ongoing maintenance and technical support, ensuring that the automation operates efficiently and reliably over the long term.
How to Choose the Right Welding Process for the Project?
Selecting the proper welding process is a critical step in the planning of any fabrication or construction project. A poorly chosen welding process can result in poor joints, production delays and increased costs. Therefore, it is essential to consider several factors before deciding which technique to use. The following are the key aspects to consider when selecting the welding process.
1. Kind of Material
The type of material to be welded is one of the most influential factors in the choice of welding process. Different materials require specific welding techniques due to their physical and chemical properties. Common materials and their preferred welding processes include:
- Steel: Arc welding (MIG or TIG) is common for carbon steel and stainless steel. Resistance welding is suitable for thin sheets.
- Aluminum: TIG welding is generally preferred for aluminum due to its high quality and control in fusion. MIG welding is also used, especially in production applications.
- Plastics: For the welding of plastics, ultrasonic and friction welding methods are the most common, as they do not require external heat input.
- Composite materials: Welding of composite materials, such as carbon fiber, is often done using adhesives or mechanical joining techniques, as conventional welding can damage the structure of the material.
2. Piece Thickness
The thickness of the parts to be welded also influences the selection of the welding process. Generally, welding methods can be classified according to the thickness of the material:
-
Thin materials (less than 3 mm): Welding processes such as MIG, TIG or resistance welding are ideal, as they allow precise heat control and minimize the risk of deformation.
-
Thick materials (greater than 6 mm): Arc welding, such as the SMAW (manual arc welding) process, or gas welding are more appropriate, as they allow for greater weld penetration.
-
Multi-layer joints: In cases where multiple layers of material need to be welded, processes that offer good fusion and penetration, such as MIG or TIG, should be considered.
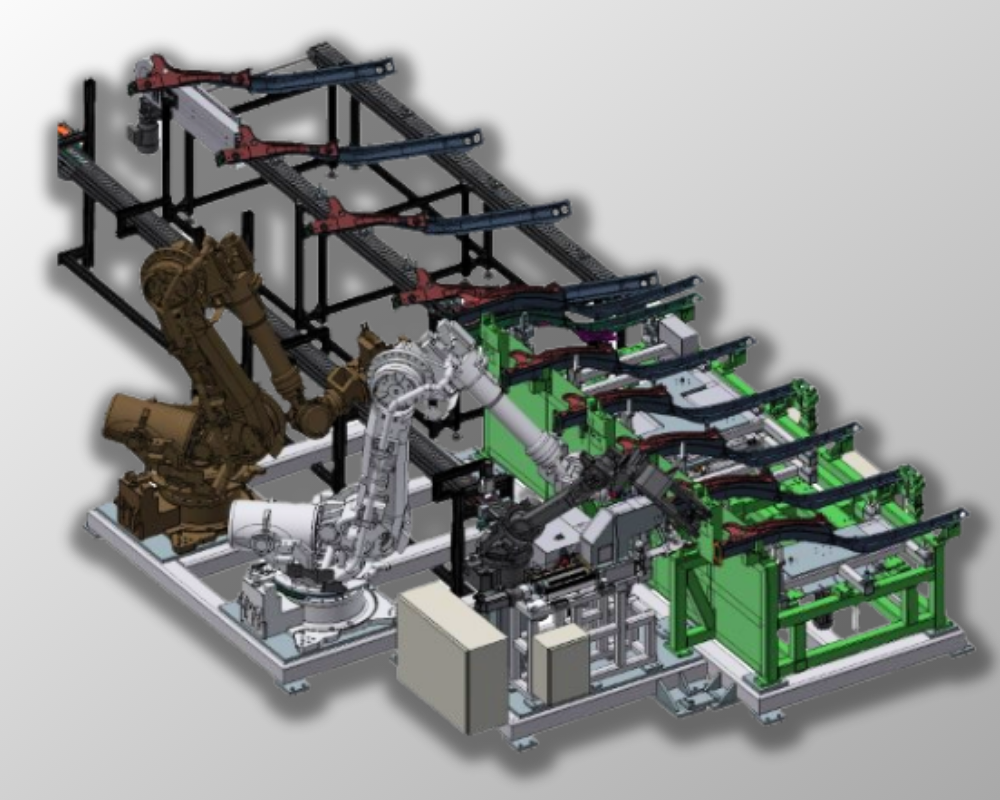
Photo: general view of welding installation of beams (MAG and Resistance)
3. Project Requirements
Each project has specific requirements that may influence the selection of the welding process. These include:
-
Regulations and standards: Some industries, such as aerospace and automotive, have strict regulations on weld quality. It is important to ensure that the chosen process complies with these regulations.
-
Service conditions: The end application of the welded product must also be considered. For example, in applications where parts will be exposed to extreme temperatures or corrosive environments, processes and materials must be selected that offer adequate resistance.
-
Aesthetics: In some cases, the appearance of the weld may be an important factor. Processes such as TIG, which produce cleaner, more aesthetically pleasing welds, are preferable in applications where appearance is crucial.
4. The available budget and the required experience.
The cost of materials, equipment and labor, as well as the training and experience of the team that will implement the project are also determining factors in the decision.
In conclusion, the automation of welding processes represents a strategic investment for companies seeking to improve their competitiveness in the market. It achieves greater precision and consistency in the joints, reducing the possibility of human error and quality defects. In addition, production times are shortened considerably, increasing operational efficiency and enabling the company to achieve improved production targets. On the other hand, automation also enhances workplace safety by minimizing operator exposure to hazardous environments.
(Continue Reading)
Click on the image to read the second part of this special on Industrial Welding Process Automation:
KEY ELEMENTS AND IMPORTANT PRIOR DECISIONS.